The distribution range of the Atelopus genus can be divided in 4 altitude ranges.
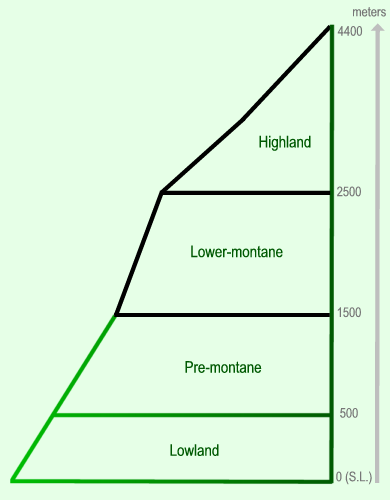
Highland 2500 - 4400 meter a.s.l. (Above Sea Level).
Lower-montane 1500 - 2500 meter a.s.l.
Pre-montane 500 - 1500 meter a.s.l.
Lowland 0 - 500 meter a.s.l.
Highland
The Atelopus species are distributed throughout a large range of altitudes. There are populations living above 4200 meters above sea level (a.s.l.) and populations almost at sealevel. Most Atelopus species live in the Andean mountains. These highland (or páramo) Atelopus species mainly live in Colombia and Ecuador. They must be very well adapted to the weather conditions in the Andean mountains as they are often very extreme. The first Atelopus infected with Chytrid was found in 1980 and many species have been wiped out since. This is why there are many species of which nothing is known about their natural habitat, because they got wiped out before scientists where able to research and descibe them in their natural habitat.
Lower-montane
Populations were often found in cloud forests. Cloud forests usually are very cloudy, humid and misty. A population of Atelopus varius was living near the popular Monteverde Cloudforest in Costa Rica. This population disappeared between 1990 - 1992.
Pre-montane
The habitats can differ alot at this altitude range. Rainforests are often found at this altitiute but there also areas with only small patches of forest near streams. Atelopus zeteki could be found in such an area.
Lowland
Tropical rainforest with small streams. Temperatures above 30 degrees celsius during the day are quite common.